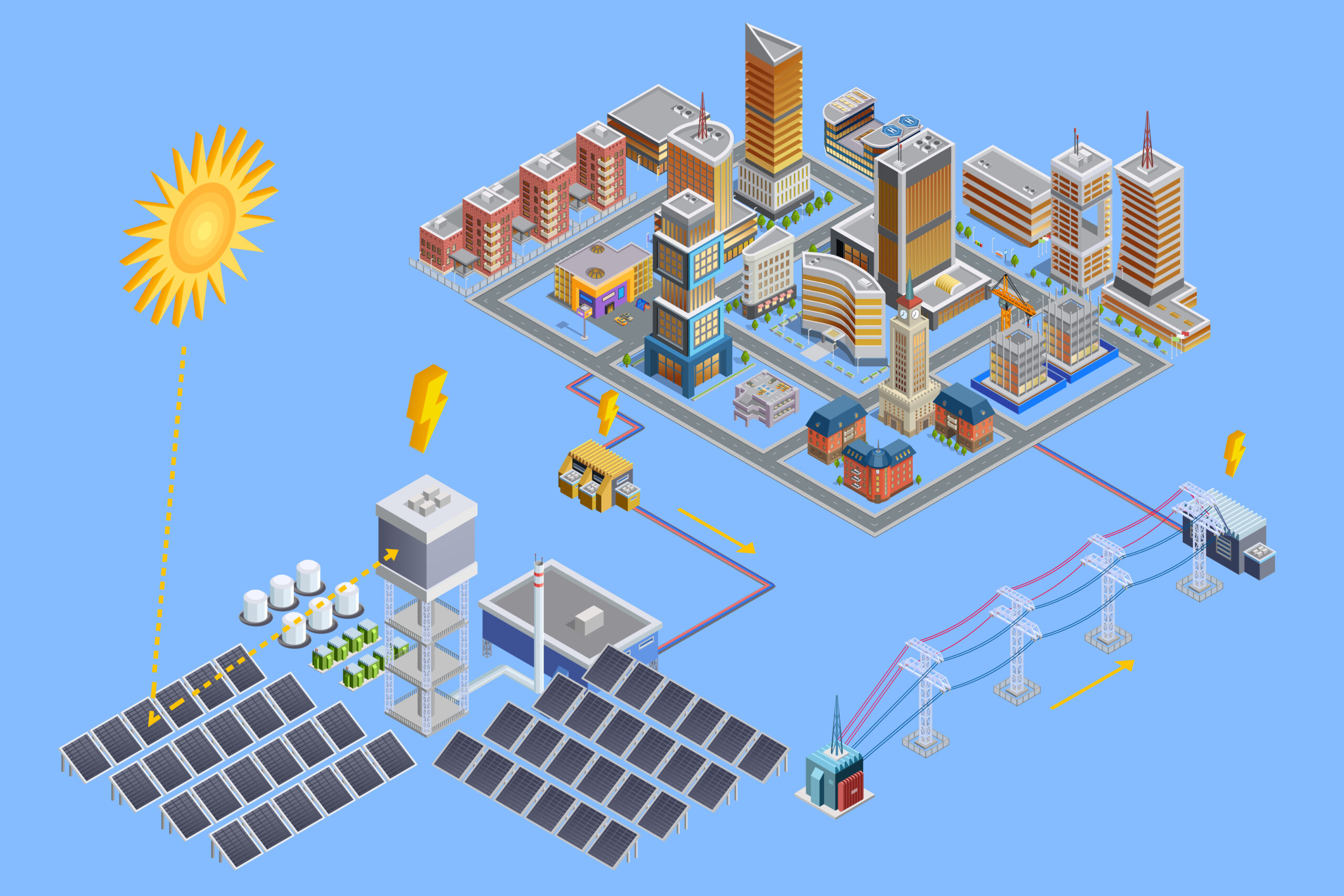


Understanding the Solar Business Opportunity
Solar panels are leading the charge in the renewable energy revolution, presenting a significant solar business opportunity for entrepreneurs looking to enter the thriving solar energy market.
Both businesses and residents are interested in reducing emissions, lowering energy costs, and contributing to ecological wellness. The United States, China, and Japan are heavily investing in renewable energy and producing jobs in solar technology at a rapidly accelerating rate. Biden’s plan to decarbonize the US economy is well underway, and will hopefully continue into the next administration.
In this article, we will cover solar energy and its scientific constituents, discuss the features, benefits, and challenges to installing and maintaining solar, and the solar business opportunities and residential possibilities that can result from investing in this segment of the renewable energy sector.
Solar Cell vs. Solar Panel
Solar cells and solar panels are both components of solar energy systems but differ in terms of efficiency, cost, and application. A solar cell directly converts sunlight into electricity, while a solar panel is an array of cells that generates a larger amount of power. Solar cells tend to be more efficient but are expensive, while solar panels are cost-effective and better suited for large-scale applications. Understanding the difference between solar cell vs solar panel technology is crucial for making informed decisions about the most appropriate and cost-effective solar solution.
Types of Solar
Solar panels are generally comprised of photovoltaic cells made of silicon. Crystalline silicon is the most ubiquitous material used to produce these cells.
From an energy conversion standpoint, crystalline silicon solar cells can attain up to 22% energy conversion efficiency under standard operating conditions. Testing them in vivo during these operating conditions will further propel the technology penetration.
There are two main subsets of crystalline-made solar panels: monocrystalline and polycrystalline. In addition to these two subtypes, there are thin-film solar panels, an alternative option that’s also budget-friendly, comparatively. Below we compare the pros and cons of each of these three.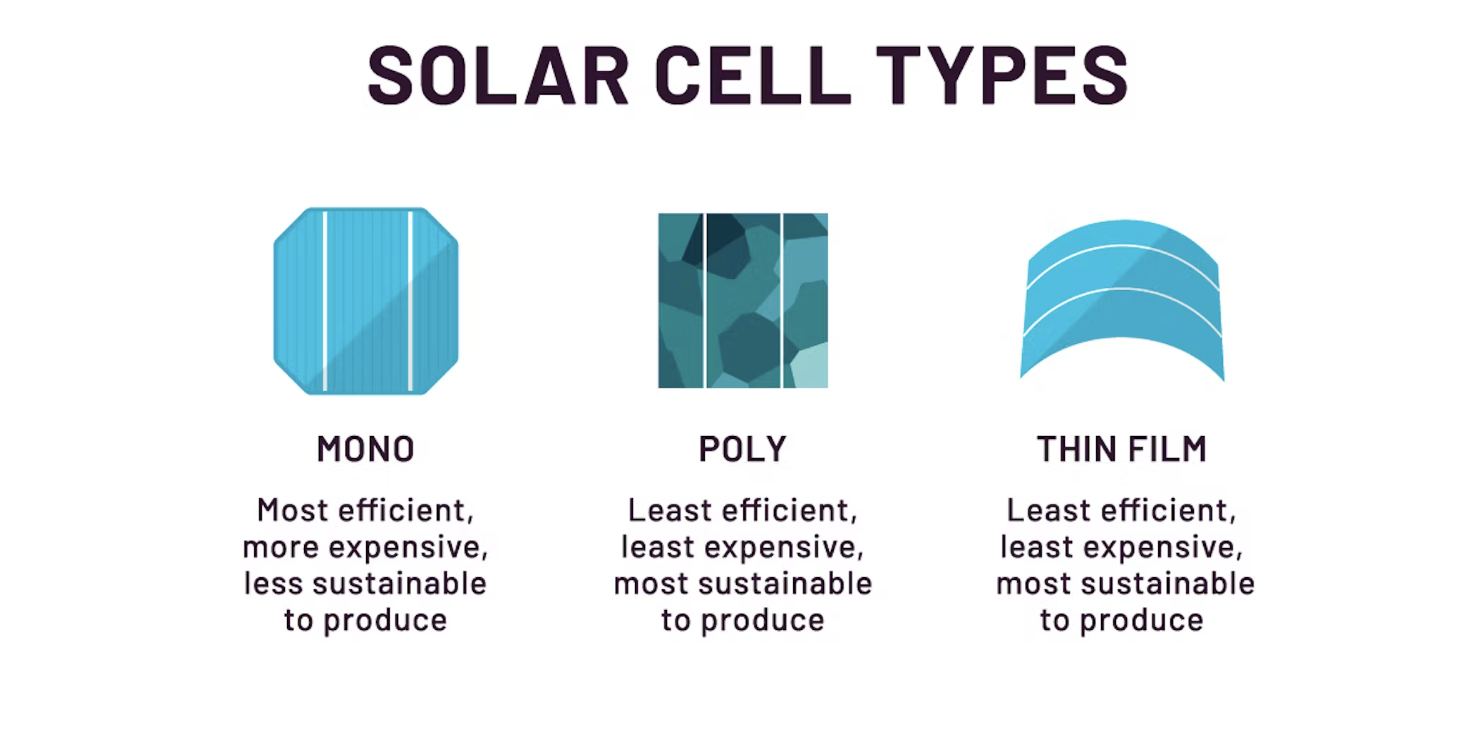 Image by Unbound Solar.
Image by Unbound Solar.
Monocrystalline Panels
These units can reach up to 24% energy conversion efficiency, meaning they produce more kilowatt-hours of electricity. They are in general more powerful than polycrystalline panels. They’re produced via a single crystal growth method, which is highly affordable in and of itself.
In addition to their efficiency, monocrystalline cells have high longevity and durability, high embodied energy per panel,* and low overhead costs. They’re also more widely available than polycrystalline panels.
However, while operating costs are low with monocrystalline panels, the single-crystal process itself is an expensive one.
*Embodied energy is an umbrella metric, which takes into account all the energy required to extract, process, and transport such materials as crystalline silicon. As an umbrella term, it includes energy factors that both emit and don’t emit greenhouse gases – so it includes carbon. Embodied carbon specifically addresses sustainability factors, measuring only the carbon emissions from any given energy source.
Polycrystalline Panels
Polycrystalline panels are in general less efficient than their monocrystalline counterparts. This means you need more panels for the same amount of energy output. They are lower in price due to a simpler manufacturing process. They have high durability and longevity, though slightly lower than monocrystalline panels. One of the main drawbacks of using polycrystalline is their weather sensitivity; they are less productive in heat.
Thin-Film Panels
These are the simplest solar panels: they’re cheap, highly energy-efficient, require less material (with none of their components being toxic), generate less waste, and have a simple, distilled manufacturing process as compared to crystalline silicon. There are actually three different subtypes of thin-film panels: amorphous silicon, cadmium telluride, and copper indium gallium selenide.
Factors Impacting Solar Panel Efficiency
Since solar panels convert sunlight into thermal and/or electrical energy, it is the amount and concentration of sunlight that determines solar panel efficiency. Included in that consideration are a host of specific factors that can affect the efficiency of all of the abovementioned types of solar panels.
1. Orientation
The best place to orient solar panels for maximum efficiency for buildings north of the Equator is directly south. Conversely, for buildings south of the Equator, the best angle is directly north. This allows for maximum, consistent exposure to sunlight.
2. Thermal Cycling
Thermal cycling is equivalent to operating temperature. Higher operating temperatures lead to reductions in efficiency, specifically because the panels are already exposed to heat.
3. Inverter Efficiency
Inverter efficiency is the percentage of a solar panel’s usable power, calculated as the difference between the input of energy (DC) and the output of energy (AC). If the inverter isn’t operating at peak efficiency, the solar panel will be less efficient.
4. Environmental
Humidity and temperature affect the power output of solar panels. The higher the heat, the less efficient the output, and the lower the temperature, the more efficient the output.
Solar Business Opportunity: Residential vs. Commercial
Armed with the knowledge of how solar works, let’s discuss the benefits of owning solar panels for both commercial and residential properties. The motives for investing in solar for each are largely different, but there are some aspects that are the same, like increased property values, as you’ll see below.
Applications & Benefits for Business
There are a plethora of benefits that solar panels offer businesses. Among them include great ROIs, augmented cash flow, increased business value, and more.
.jpg)
Let’s discuss the main selling points of each:
1. ROI
Solar panels have a relatively short ROI, with savings in utilities generally matching the investment made within 3-4 years. Of course, investment and savings both depend greatly on the scale of the enterprise and installation locations.
2. Augmented Cash Flow
Monthly energy bills will uniformly go down with solar panels, particularly high-efficiency panels with low down payments under the right environmental conditions.
3. Increased Business Value
The trend towards renewable energy makes investing in solar a business opportunity. Studies show that solar-equipped buildings have higher property values, and the demand for solar-equipped buildings is definitely on the rise.
4. Tax Credits
There are federal tax credits that you can obtain for installing solar, particularly given the new Infrastructure Bill.
5. Going Green
Consumers are more eco-conscious than ever, so it benefits enterprises everywhere to live up to customer expectations and sustainability standards. While we cannot predict the energy landscape decades from now, we can safely say that by going green now you can safeguard your business and your brand image from the changing cultural tides.
Residential Benefits
The U.S. Department of Energy has created a list of solar energy’s benefits for residential applications. Some of these are very similar to the benefits of commercial solar, but there are some key additions. .jpg)
1. Increased Savings
As a homeowner with solar power, you’ll save on electricity consumption and therefore utility bills, leading to more available cash. These depend on several factors, some of which we’ve addressed above, including the size of your solar installation package, whether you’ve purchased or leased your system, the amount of available sunlight, environmental conditions, and where your panels are oriented. If all of these conditions are ideal, you’ll save a considerable amount of money.
2. Increased Property Value
Solar panels are home upgrades, so you’re increasing your home’s value by installing them. A Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory study showed that solar panels can boost a home’s value by approximately USD 15,000.
3. Ecological and Environmental Benefits
Each kilowatt-hour of solar energy offsets greenhouse gas emissions and saves water. Additionally, investing in solar now can help future-proof your home as new legislations are passed.
Challenges with Solar

Infrastructure
A large-scale solar industry will have substantial, broad-reaching effects on the US economy. But first, we need the infrastructure to support that energy.
The US Department of Energy needs to retrofit the grid infrastructure to handle the large influx of solar energy applications. The clean energy plan that’s currently being implemented is a solution to this problem, but one that will likely take some time (and considerable capital) before it pays off.
Recycling
Technically, the need for an efficient nationwide recycling program to cope with the amount of material from defunct solar panels is also an infrastructural one. Panels contain toxic metals, but they also contain highly valuable metals and minerals that can be recycled and repurposed.
The problem is, we don’t have the system to handle such needs, and there currently isn’t much official regulation. The solution is to invest in innovative technologies that can make recycling more practical and to create jobs around solar recycling and repurposing – hiring specially qualified workers to handle these materials.
Supply Chain
We have China’s innovative industrial policies to thank for photovoltaics becoming the most affordable electricity generation technology in many parts of the world. However, these same policies have led to the concentration of solar panel manufacturing in one nation.
Today, China controls about 80% of the key manufacturing stages for solar panels. That number is expected to rise to 95% in the coming years according to the IEA Special Report on Solar PV Global Supply Chains.
As we saw during the pandemic, high commodity prices and supply chain bottlenecks can have a dramatic effect on global economies. With all our solar energy eggs in one basket, so to speak, we run the risk of solar panel production and trade grinding to a halt in the event of economic sanctions, war, outbreaks, and other such disasters.
If we want to truly reach the IEA’s goal of net zero by 2050 and make our renewable energy industry more resilient, countries must invest in developing their own solar infrastructure. As the IEA Executive Director Fatih Birol states: “As countries accelerate their efforts to reduce emissions, they need to ensure that their transition towards a sustainable energy system is built on secure foundations. Solar PV’s global supply chains will need to be scaled up in a way that ensures they are resilient, affordable, and sustainable.”
The Verdict: There Are Massive Benefits to Investing in Solar
The benefits of solar energy far, far outweigh the difficulties, all of which are solvable. These benefits include a dramatic reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, the creation of new jobs, increased ROIs and reduced energy bills, tax incentives, higher property values, and more.
As global leaders invest more in solar energy, the rest of the world will follow suit. Thanks to innovative partnerships between solution providers and industry leaders, we can help curb some of the destructive effects of coal and gas on both local and global ecosystems. It’s also highly lucrative to invest in solar energy now, as the trends are all accelerating in the symbolic race for innovation.

